Scar Treatment
When the integrity of the skin is impaired due to any reason such as trauma or surgery, a scar develops.
The scar can be closed with sutures, can heal spontaneously under dressings, or can be covered with tissue grafts transplanted to the wound area using various techniques.
Regardless of the cause of the wound or method used to close the wound, a repair process begins in the repair area. It may take 1-2 years for a scar to take its final form. The scar fades into skin color over time. The initial hardness softens and becomes more homogeneous, but the wound definitely leave a significant or insignificant scar.
In the event of scar formation, it is necessary to be patient, knowing that it will change over time. It is beneficial to be under the supervision of a plastic surgeon during the waiting period.
Scar correction is an important matter in plastic surgery, and many different techniques are used to achieve a more aesthetic appearance.
Many factors, in addition to the plastic surgeon, play a role in the formation and treatment of a scar, as explained below.
What Are The Causes of Scarring?
- Accident and injury
- Scars caused by surgical interventions
- Burn
- Infection
- Bite scars
- Post-acne scars
- Rash scars after chickenpox and other similar diseases
How Is A Scar Treated?
There are various approaches to the treatment of scars. The scar may heal spontaneously, or treatment procedure may differ depending on the scar’s condition. For example, scars left by mammoplasty or gynecomastia operations heal more quickly. Although a scar on the face is not hypertrophic, it can become an aesthetic problem due to its visibility.
Treatment procedures intended for scars on the face are similar to the procedures performed to treat scars on the hand or other part of the body. In this context, non-surgical treatments help make the wound less visible. Although there is no treatment method that completely removes scars on the hand and face, the treatment procedures turn scars into a more acceptable form.
The cosmetic surgery procedures have doubled since the early 21st century. 92% of these cosmetic procedures were performed on women. Of course, the condition of the wound and the speed of patient’s recovery are two factors that influence this process. A specialist physician should be consulted to get more information about the treatment of surgical incision scars and other scars.
Source: Wikipedia
How Scars Other Than Surgical Incision Scars Treated?
Scar treatment varies depending on the nature of the wound (burn scar, suture scar, etc.). Various procedures such as dermabrasion, the balloon method, and laser scar treatment stand out among all treatment procedures intended for surgical incision scars and other scars. You can find details on scar treatment procedures below.
Scar Treatment Procedures
- Doing nothing: It is not yet possible to completely remove a scar and enable the patient to look as if he/she had never been injured. Scars can sometimes get worse when they are attempted to be corrected. Therefore, it is of critical importance to listen to the advice of experienced plastic surgeons, and not to follow the recommendations of any other people.
- Complete removal of the scar and its reconstruction with sutures: The scar is completely removed and the remaining intact edges re-sutured using a more appropriate surgical technique and suture material.
- Removing and Resuturing the Scar along a Zig-Zag Line: It is a technique commonly used to change the direction of a wound and make it less noticeable.
- Tissue expansion with a balloon: A balloon intended to expand the tissue is surgically placed beneath the intact skin adjacent to the wound. The tissue expander is initially empty. In a few weeks, the balloon is inflated with saline water injections into the balloon. The skin starts expanding along with the inflated balloon. When adequate tissue expansion is achieved after a few months, the wound is removed with a second surgical operation, and the adjacent expanded normal skin is pulled to this area to cover the scar.
- Laser treatment for scars: Surgical incision scars and other scars can be treated with laser. In the late stage, it can be used to remove redness from the scar and for dermabrasion to remove irregularities on the scar.
- Dermabrasion And Thin Skin Patch: It is a procedure performed to remove scars where color differences stand out, such as burn scars invading large areas, and self-harm scars (e.g. self-inflicted razor blade incision scars). First, dermabrasion is performed on the surface of the skin, and then thin skin patches taken from the thigh are transferred to this area, resulting in a surface that is more compatible with normal tissue. The Dermabrasion and Thin Skin Patch technique, which is the world’s first self-harm scar treatment technique that I invented and use exclusively, produces successful results.
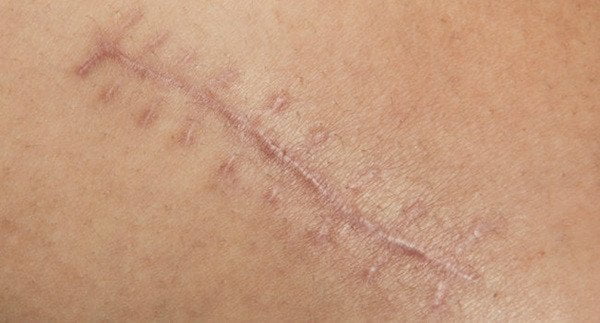
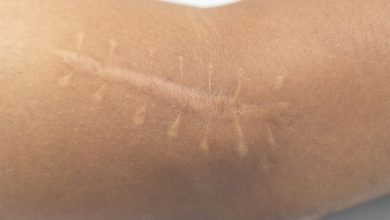
Problems Caused by Scars
- The color of a scar may be different from that of the surrounding healthy skin.
- A scar in the form of a fine line can get wider over time.
- The scar and the suture marks extending along the incision line may remain noticeable.
- The scar site may be a bit raised, pink purple in color, hard, itchy, or even painful.
- A scar that is initially small may swell and progress into the surrounding tissue within months.
- It can impair the natural contours in areas such as the lip, nasal wings, ears, eyelids, arms, and palms, and can also restrict joint movements.
Factors Affecting Scar Healing
Mechanism of Injury
In the scarring process, the extent to which the cells are traumatized is very important. When a surgeon makes a surgical incision with a scalpel, the damage to the cells is minimal, and wound healing occurs under more favorable conditions.
On the other hand, more inflammatory reactions and connective tissue formations occur during the healing phase of a wound caused by a high-energy incident, such as a traffic accident or a firearm injury, where the tissues are crushed and destroyed uncontrollably. A wound caused by cutting does not leave a scar in the same way that a wound caused by crushing, amputation, or peeling does.
A wound caused by cutting and a wound caused by crushing, amputation or peeling do not leave a scar in the similar ways.
Nature of Wound
An incision wound affecting only the skin tissue that was formed in clean conditions leaves a scar that differs from scars left by crushed wounds covered in dust and dirt which affect subcutaneous tissues in addition to the skin. Blood circulation and tissue healing are more difficult in areas with extensive tissue crushing and tissue loss.
Location of Wound
Wounds do not heal in the same way in all areas of the human body. A wound in the thin and loose skin of an eyelid does not leave a noticeable scar, while wounds in other areas, such as the anterior chest wall, neck, and shoulders, tend to leave more noticeable scars.
Direction of A Wound
The location of the wound on the face and body has a direct influence on the result. For example, a horizontal incision in the forehead parallel to the forehead wrinkles is less noticeable, whereas a vertical incision in the same area is more noticeable.
Plastic surgeons know where and in which direction the incision should be made on the body, and they plan incisions accordingly. Wounds that occur in random directions after injuries, on the other hand, are more likely to leave more noticeable scars. Changing the direction of scars is an effective method used in scar treatment.
Wound Repair Technique
Choosing the repair technique that is the responsibility of plastic surgeons is one of the important factors determining the scar, but is not the only factor.
During wound repair, “atraumatic” techniques should be used to cause the minimal harm to the cells. The subcutaneous layers should be properly repaired, without leaving dead tissues or dead spaces, and tension formations should be avoided.
Suturing the wound edges tightly together in injuries with tissue loss paves the way for bad scarring.
Suture Materials
Suture materials that are least likely to cause infection and inflammation in the body should be used.
Time For Suture Removal
If the sutures are left on the skin for longer than 5-7 days, they may leave permanent marks on both sides of the incision scar. In order not to deal with processes such as suture mark treatment in the future, it is of critical importance to support the wound with the help of sutures placed under the skin and tapes, and sutures should not be left in place for more than 5-7 days, especially in aesthetically important areas like the face.
Infection Risks
If an infection develops at the wound site, it causes more tissue reaction, connective tissue (scar) synthesis, and scarring.
Patient’s Age
Since the connective tissue cells in children are more active, the skin is tenser, and wounds tend to leave more scar. In elderly patients, on the other hand, the situation is just the contrary.
General Health Condition Of The Patient
Wound healing problems are more common in people with chronic diseases such as certain collagen tissue diseases, cancer, radiotherapy, diabetes, nutritional deficiency, and renal failure, where the environment needed for normal wound healing is not available.
Smoking
Smoking reduces blood flow in the veins in the wound area and has a negative impact on wound healing.
Çevresel Faktörler
Sun rays and other ultraviolet sources increase pigmentation and cause discoloration in the wound site. Sun protection is of critical importance throughout the healing process, especially in the first few months. Clothing and high factor sunscreens should be used to protect the wound site from the sun.
Many other factors not mentioned here influence wound healing and the features of the scar that will develop. Therefore, when a bad scar appears, its causes should be thoroughly investigated, and only the doctor or the material used should not be held responsible.
What should be done to avoid scarring?
First of all, it should be kept in mind that the healing process of wounds (surgical scars, cuts, burns, skin injuries, and so on) may take 1-2 years; so you should be patient in this regard. It should be remembered that the wound will draw more attention in the first postoperative days due to its pink, red, or purple color, but will draw less attention as the color fades over time.
To avoid scarring, the plastic surgeon’s recommendations should be followed, and the following factors should be taken into consideration.
- Sun Protection: The effect of sun rays on the wound can be considered a negative effect. UV rays in sunlight or solarium devices can stimulate the pigment cells at the wound site, causing the wound to get darker than normal. The wound site should be protected from the sun after it has formed, especially in the first 2-3 months. Clothes or tapes can be used for this purpose. Sunscreen with a protection factor of 50 should be applied to sun-exposed areas several times a day, especially during the summer.
- Medical tapes: Medical tapes (such as steri-strip) have been reported to improve wound healing when applied to non-open and healed wound scars for a period of 3-6 weeks.
- Ointments: A variety of creams with silicone or herbal ingredients are used to manage the repair process and reduce erythema in the wound site. The method and duration of application is determined by the physician based on the nature of the wound.
- Silicone Gel Sheet: 1-2 mm thick silicone layers can be used to cover the wound. Since continuous application may cause skin irritation, it is necessary to take interruptions from time to time.
- Massage: Manual massage on the wound helps soften and better remodel the connective tissue that has formed in that area.
- Pressure Treatment: It is useful to apply a certain degree of pressure with tubular bandages or special clothing to wounds such as deep burns that tend to swell.
Does A Scar Disappear Over Time?
There are various factors that influence the possibility of scar disappearance. This possibility varies depending on the depth and nature of the wound, as well as the time elapsed since the injury was performed. Mild scars may fade over time, but in cases where the integrity of the skin has been is impaired, it is not possible for the scar to disappear over time.
Poor Wound Healing (Hypertrophic Scar)
In normal wound healing, a balance occurs between connective tissue synthesis and tissue destruction when the wound integrity is restored and the activities of the cells involved in wound repair decrease.
In cases of abnormal or poor wound healing, the connective tissue synthesis is prolonged excessively despite wound closure. In the weeks following the injury, a hard mass starts developing in the wound area, which can be raised, red-purple, itchy, and painful.
Hypertrophic scar formation or, in a more advanced form, keloid formation is caused by various factors. There are many factors playing a role in poor wound healing, such as genetic characteristics of the person, age (children), location of the wound on the body (anterior chest wall, shoulders), the mechanism of formation of the wound (deep burns), and conditions for repair or healing of the wound.
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment method. Silicone therapies, pressure treatments, lesion treatment with cortisone, and a variety of other treatment methods are used.
Surgical removal of the hypertrophic scar or keloid tissue is not the first treatment option. It can, however it can be performed under special conditions after taking some precautions.